Sound classification
1. Description général
Classification automatique des sons
Développement d'un système général de classification comprenant:
- extraction de descripteurs audio
- apprentissage automatique de paramètres de classes
- classification automatique de nouveaux sons à partir des paramètres appris
Evaluation pour le cas particulier de la classification des échantillons d'instruments de musique
2. Méthode proposée
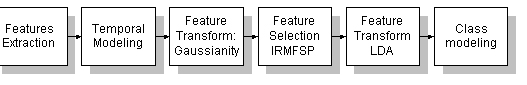
Figure 1. Overall schema of sound classification module
Le système développé dans le cadre du projet CUIDADO, doit permettre la classification automatique des sons à partir
de définition de classes préalable, ainsi que l'apprentissage de ces classes en lignes (par définition de l'utilisateur).
Pour celà, un système complet d'apprentissage/évaluation a été créer:
- Extraction des descripteurs
- Apprentissage des modèles de classes
- sélection automatique des meilleurs descripteurs,
- transformation des descripteurs,
- création des modèoles de classes
- Evaluation: mesure de l'appartenance d'un son donné à une classes définie
2.1. Feature extraction:
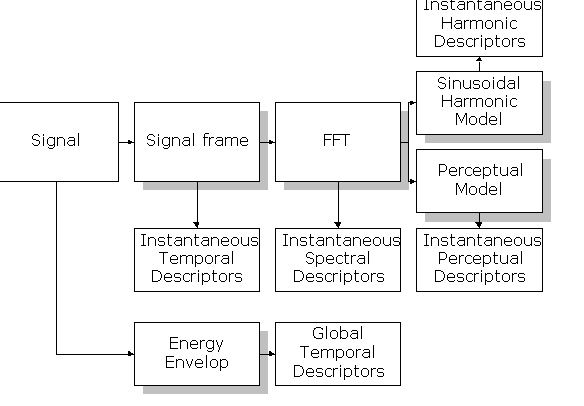
Figure 2. Features extraction
For each sound, a large set of sound descriptors are extracted including
- temporal shape descriptors
(attack-time, increaqse/decrease time, modulation, ...)
- energy descriptors,
- spectral descriptors
(centroid, spread, skewness, kurtosis, roll-roff, ...),
- harmonic descriptors
(fundamental frequency, noisiness, inharmonicity, odd-to-even energy ratio, deviation, ...),
- perceptual features
(loudness, specific loudness, roughness, ...).
The evolution along time of a specific features is then modeled by a temporal modeling modules.
Each sound is then represented by a feature vector.
2.2. Learning
Feature selection: Inertia Ratio Maximization with Feature Space Projection (IRMFSP)
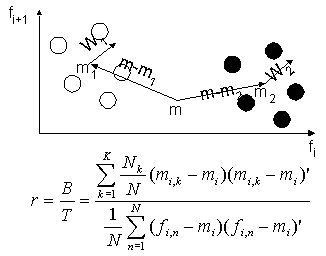
Figure 3. Feature selection
In order to determine the most appropriate features to describe a specific taxonomy, a "feature selection" module is used.
- This module select the best features according to the value of the
Between class inertia to the Total inertia.
The largest this ratio is, the most discriminant is the feature.
- The whole feature space is then projected on the first selected feature
(the one with the largest ratio value) and the process repeated for the selection of the next value.
Feature transform:
Before class modeling,
- a Box-Cox transform is applied in order to maximize feature's gaussianity
- a Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) is applied to the feature space in order to maximize class separation
Class modeling:
Different kind of classifiers are compared
- Flat gaussian classifier
- Flat KNN classifier
- Hierarchical gaussian classifier
- Hierarchical KNN classifier
- Binary Decision Tree
2.3. Evaluation:
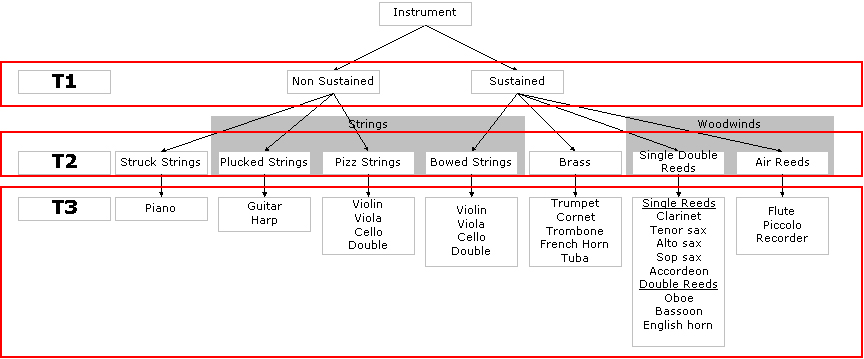
Figure 4. Instrument sounds taxonomy
Six different databases have been used for the evaluation, for a total of 4163 sounds, covering 27 instrument classes.
Three different classes taxonomy have been used:
- T1: sustained/non-sustained sounds,
- T2: instrument families,
- T3: instrument names.
Results:
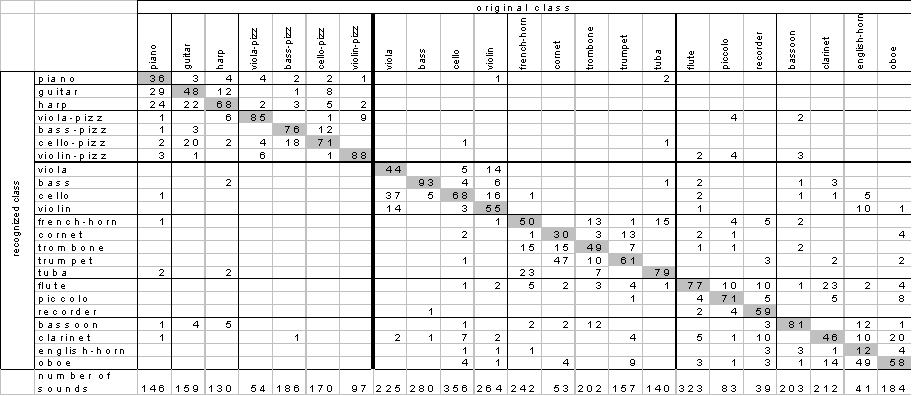
Figure 5. Confusion matrix
The best results are obtained using the
- hierarchical gaussian/KNN classifiers.
- hierarchical KNN classifiers.
Recognition rates for 27 instruments:
- at T1: 99%,
- at T2: 84%,
- at T3: 64%.
Related publications
- Geoffroy Peeters, Stephen McAdams, Perfecto Herrera Instrument Sound Description in the Context of MPEG-7
ICMC2000 Berlin (Germany) August 2000
- Geoffroy Peeters, Xavier Rodet Automatically selecting signal descriptors for Sound Classification
ICMC 2002 Goteborg (Sweden) Septembre 2002
- Perfecto Herrera, Geoffroy Peeters, Shlomo Dubnov Automatic Classification of Musical Sounds
Journal of New Musical Research 2003, Vol. 32, No. 1, pp 3-21
- Geoffroy Peeters, Xavier Rodet Hierarchical Gaussian Tree with Inertia Ratio Maximization for the Classification of Large Musical Instrument Databases
DAFX03 London, UK 2003 September 8-11
- Geoffroy Peeters Automatic Classification of Large Musical Instrument Databases Using Hierachical Classifiers with Inertia Ratio Maximization
115th AES Convention New-York, NY, USA 2003 October 10-13
- Geoffroy Peeters A large set of audio features for sound description (similarity and classification) in the CUIDADO project
CUIDADO I.S.T. Project Report 2004