simplify(a,f,x,y,...) ¯ 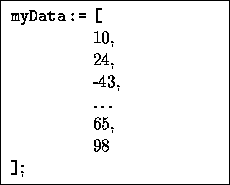 ¯
¯
type(a,f,x,y,...) 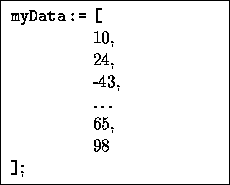
`type/f`(a,x,y...)
convert(a,f,x,y,...) 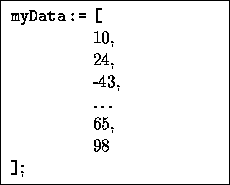
`convert/f`(a,x,y...)
simplify(a,f,x,y,...) 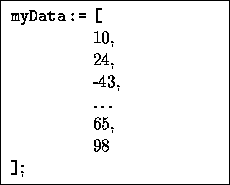
`simplify/f`(a,x,y...)
combine(a,f,x,y,...) 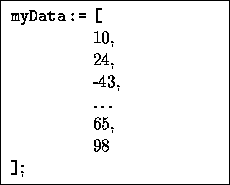
`combine/f`(a,x,y...)
define(a,f,x,y,...) 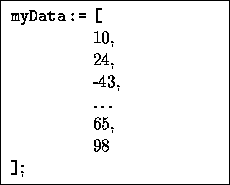
`define/f`(a,x,y...)
`print/f`(x,y,...) 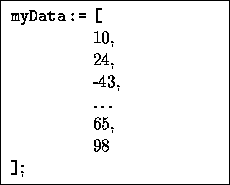
f(x,y...)
evalf(a) ![]()
`evalf/kind_of_a`(a)
?foo ![]()
`help/text/foo` := TEXT(``,...,``);
?foo,x ![]()
`help/foo/text/x` := TEXT(``,...,``);
readlib(pname) ![]()
read ``.libname.`/`.pname.`.m`
+ remember table
with(lname) ![]() 'eventuellement lecture de
'eventuellement lecture de `lname.m`
+ affectations suivantes:
lname[foo] := readlib(`lname/foo`);
foo := lname[foo];
(pour toutes les fonctions foo de la biblioth`eque)