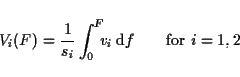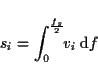



Next: 6.3 Other Manipulations
Up: 6. Manipulation of Spectral
Previous: 6.1 Interpolation
6.2 Amplitude Manipulations
An obvious type of manipulation of spectral envelopes is amplitude
manipulation . To describe that whole class of manipulations, we only
need to define the two basic operations of addition and multiplication
of spectral envelopes. This is straightforward if we formally define a spectral envelope as a
real function v(f) with domain
 :
:
If the spectral envelope is in spectral representation (section 4.3), we
get to the functional interpretation by linear interpolation as in
equation (5.1). If it is in precise formant representation,
we can evaluate the formant function (equation (4.1))
directly, if it is in filter coefficients, we convert it to spectral
representation.
With these operations, we can effect manipulations such as
amplification and attenuation, or spectral tilting, as explained in
the following.
- Amplification and attenuation
-
Amplification and attenuation of spectral envelopes is effected by a
multiplication by a factor greater or less than one, respectively.
Multiplication with a function over frequency (i.e. with a spectral envelope)
instead of a constant factor, thus doing frequency selective
amplification or attenuation , essentially amounts to applying a
filter to the spectral envelope.
- Tilting the spectrum
-
The overall slope of the spectrum of a speech or instrument signal
is called spectral tilt . For speech, it is among others
responsible for the prosodic feature of
accent , in that a speaker modifies the
tilt (raising the slope) of the spectrum of a vowel, to put stress
on a syllable [Dog95]. For instruments, it can be
dependent on dynamics, the relative force with which the instrument
is played. Spectral tilt is measured in
decibel per octave.
To apply a given spectral tilt t to a spectral envelope
v, we have to first normalize the tilt per octave to a tilt tm over the whole range of the spectral envelope up to
fm = fs / 2 (half the
sampling rate):
Then, the additive decibel value tm is converted to a
multiplicative amplitude factor ta:
To effect the tilting of a spectral envelope v(f), we multiply by a ramp spectral envelope vt (f) ramping from 0 to ta:
| tiltt (v) |
= |
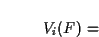 |
(6.3) |
| vt (f) |
= |
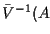 |
(6.4) |




Next: 6.3 Other Manipulations
Up: 6. Manipulation of Spectral
Previous: 6.1 Interpolation
Diemo Schwarz
1998-09-07
![]() :
: