Multi-channel equalization
Unlike traditional equalization schemes that aim at calculating
filters for each individual loudspeaker without reference to the reproduction
context (i.e. position and properties of the virtual sources), the multi-channel
equalization scheme proposed here aims at controlling the sound field
produced by the entire array of loudspeakers with reference to a given
virtual source.
To do so, each loudspeaker is measured along an array of microphones.
Sound field control is achieved by iteratively calculating a set of filters
that will, once applied to the loudspeakers, minimize the quadratic difference
between the sound field produced by the loudspeaker array and a given
target for all of the microphone positions. The target is calculated for
each microphone position by applying the laws of propagation between the
virtual source being synthesized and the microphone array. A filter data
base containing all of the virtual sources one wants to synthesize can
then be put together, to be accessed in real time during playback.
Above Left: Characterization of
a WFS reproduction setup made of 4 adjacent MAPS (Multi Actuator
Panels) forming a 32 transducer array in the Espace de Projection
at IRCAM.
Above Right: Top view of the measurement configuration. The black
dots correspond to 32 loudspeakers; the red circles correspond
to 48 omnidirectional microphones; the blue circle represents
the target virtual source situated 3m behind the loudspeaker array.
|
PLANE WAVE
|
Before Equalization Procedure
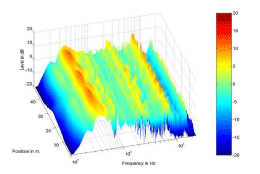
|
After Equalization Procedure
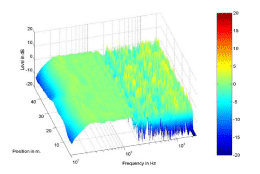
|
POINT SOURCE
|
Before Equalization Procedure
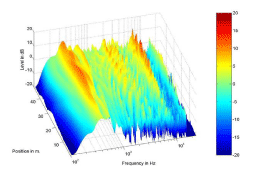
|
After Equalization Procedure
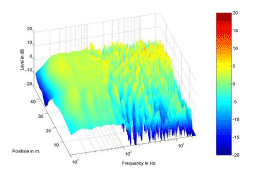
|
Above: Frequency responses recorded
along the microphone array for two different virtual sources
|
|



